
Non-central moment of the specified order. Taking a continuous beam as an example, the conventional MDM begins by assuming that each joint of a structure is fixed and subject to a fixed-end moment (FEM). If random variablesX1 : : : Xndened on a joint probability spacehave nite rst moments EX1+ +Xn EX1 + +EXn (3) without any further assumption.
> import numpy as np > from scipy.stats import norm > import. 1 First moment method Recall that the expectation of a random variable has an elementary, yet handy prop-erty:linearity.
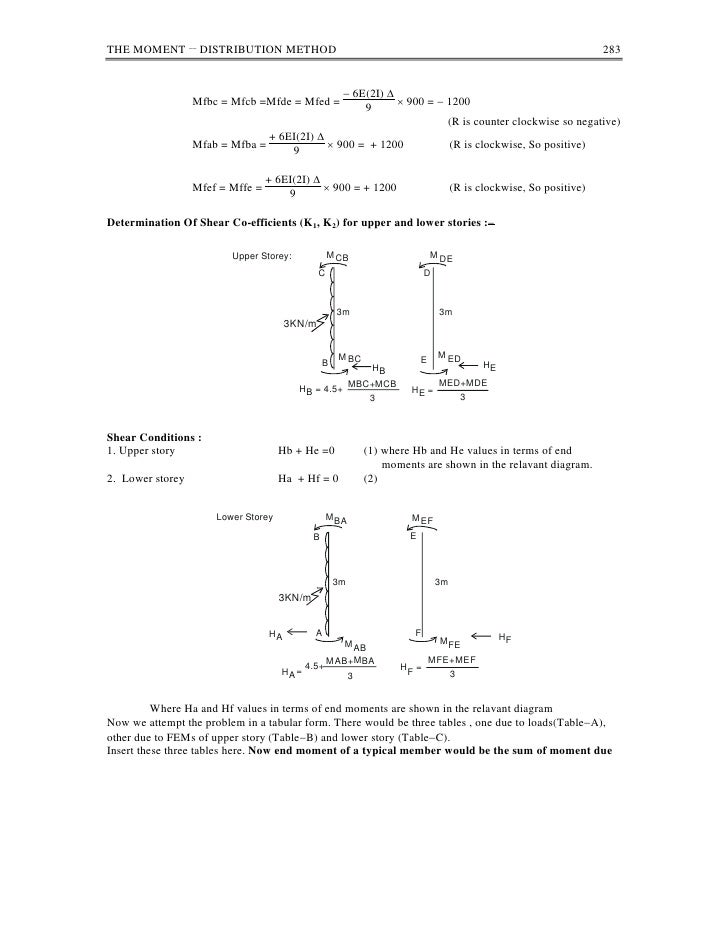
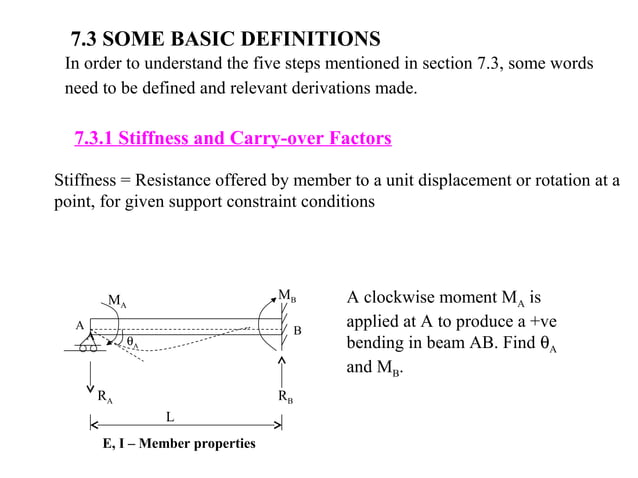
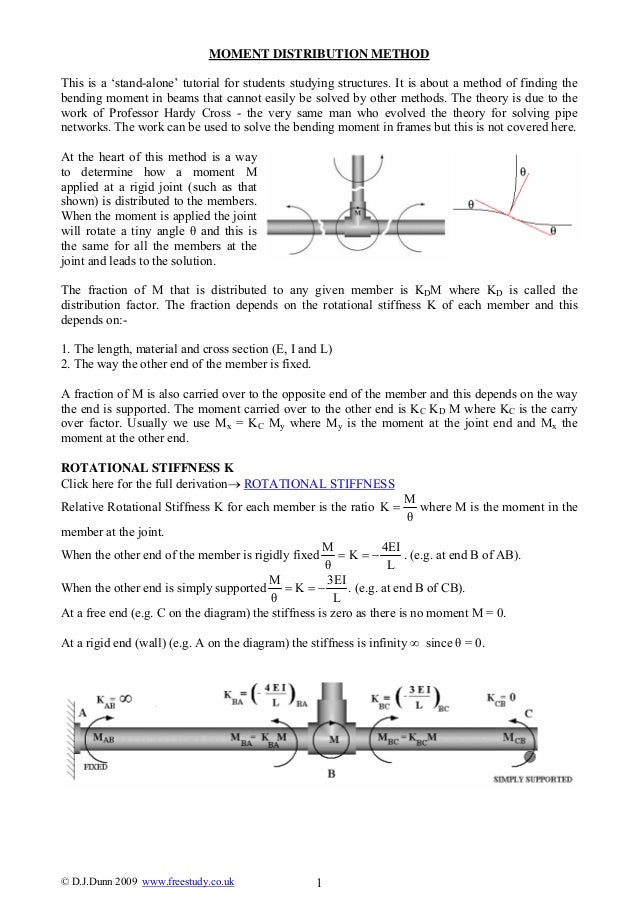
Inverse survival function (inverse of sf). To shift and/or scale the distribution use the loc and scale parameters. Percent point function (inverse of cdf - percentiles). The conventional moment distribution method is revitalized with a new approach which requires only one-cycle of balance and carry-over and no iteration. Solution In the first step, calculate fixed end moments. Assume EIto be constant for all the members. Draw bending moment diagram for the frame. To illustrate the one-step approach, three examples are given herein, namely a continuous beam, a non-sway portal frame and a simple sway frame. Example 20.1 Calculate reactions and beam end moments for the rigid frame shown in Fig. Survival function (also defined as 1 - cdf, but sf is sometimes more accurate). The moment-distribution method is carried out on a working diagram. Log of the cumulative distribution function. Rvs(loc=0, scale=1, size=1, random_state=None) legend ( loc = 'best', frameon = False ) > plt. hist ( r, density = True, bins = 'auto', histtype = 'stepfilled', alpha = 0.2 ) > ax.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
